
Blood flow towards or away from the Doppler probe, reflects sound waves causing a change in frequency that is detected using the same Doppler probe. Systolic pressure can also be determined using the Doppler principle. 5, 6 Diastolic and mean pressures cannot be determined.

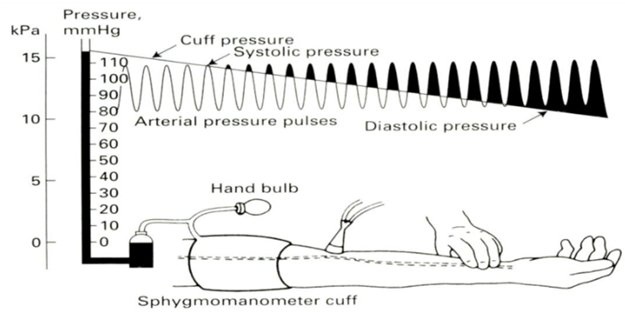
While being easy to perform, this technique has been shown to underestimate a systolic pressure of 120 mm Hg by 25%. The cuff is then deflated below systolic pressure allowing blood flow to resume this flow can then be detected using various means. At this point, the walls of the artery are opposed preventing blood flow. The cuff is inflated to a pressure above that of the arterial systolic pressure. 4 Cuffs that are too small will lead to overestimation of blood pressure and vice versa.Īn inflatable cuff for occluding the arterial supply to the distal limb Ī method for determining the point of systolic and diastolic blood pressures The cuff should be 20% wider than the diameter of the part of the limb being used (or cover two-third its length). Most commonly the upper arm is used although it is possible to use the forearm or leg when the upper arm is inaccessible, for example due to surgical requirements. Intermittent, non-invasive systems require three key components:Ī cuff is placed circumferentially around the limb. Intermittent, non-invasive blood pressure measurement 3Īlthough the System International d'unites (SI) unit of pressure is the Pascal, by convention, blood pressure is measured in millimetres of mercury (mm Hg). 2 In combination with other monitoring, it will help detect 93% of adverse events occurring under anaesthesia. Now it is part of the minimum standard of patient monitoring as recommended by the Association of Anaesthetists of Great Britain and Ireland and should be measured in all patients undergoing, and recovering from, general anaesthesia, regional anaesthesia and sedation. 1īlood pressure measurement was first used during anaesthesia by Cushing in 1901. In 1905, Nicolai Korotkoff described various sounds while auscultating over the brachial artery during deflation of a Riva Rocci cuff. Non-invasive techniques for the measurement of blood pressure have been in existence since the early 1800s, although Riva Rocci, an Italian physician, is credited with developing the first conventional sphygmomanometer in 1896. Hales first measured blood pressure in 1733 by inserting tubes directly into the arteries of animals.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
